The Ultimate Guide to Baking Yeast
Understanding yeast is essential for perfect baked goods. This comprehensive guide covers yeast types, fermentation principles, nutritional needs, and factors affecting performance—ideal for bakers and food enthusiasts.
1. How to Use High-Sugar vs. Low-Sugar Yeast Correctly
High-sugar yeast: Required for dough with >8% sugar (e.g., sweet bread, brioche, cinnamon rolls).
Low-sugar yeast: Suitable for dough with <8% sugar (e.g., French bread, pizza dough).
Pro Tip: Using the wrong yeast can lead to poor fermentation and dense textures.

2. Nutritional Requirements of Yeast
Yeast thrives with:
Carbohydrates: Primary energy source (sugars/starch).
Minerals: Magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, sodium, sulfur, and trace elements (iron, zinc, copper).
Growth factors: B vitamins (B1, B2, pantothenic acid) to boost reproduction.
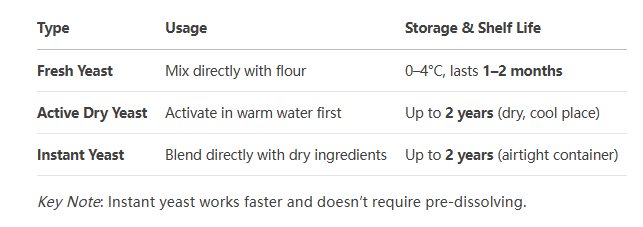
3. Types of Baking Yeast & How to Use Them
4. The Science of Yeast Fermentation
Yeast converts sugars into carbon dioxide (CO₂) and ethanol, causing dough to rise. The process:
Enzymes break down flour’s starches into sugars.
Yeast metabolizes sugars, releasing CO₂ (trapped by gluten, creating air pockets).
Alcohol evaporates during baking, enhancing flavor.
5. Yeast’s Role in Bread-Making
Leavening: CO₂ expands dough, creating a light, airy texture.
Gluten Development: Strengthens dough’s gas-retaining structure.
Flavor Enhancement: Produces complex alcohols and esters during fermentation.
Nutritional Boost: Rich in protein, amino acids (like lysine), and B vitamins.
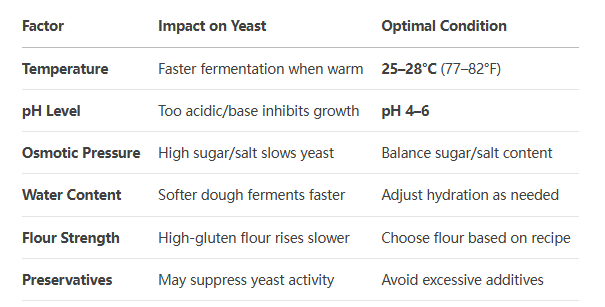
6. Factors Affecting Yeast Fermentation